 Streptodermia in children of various ages develops due to the defeat of various strains of a common microbial agent of streptococcus and a decrease in the effectiveness of immune defense.
Streptodermia in children of various ages develops due to the defeat of various strains of a common microbial agent of streptococcus and a decrease in the effectiveness of immune defense.
Characterized by the appearance of typical bubble rashes on the skin (less often mucous), filled with purulent contents. In the absence of the necessary complex treatment, streptodermia in a child progresses, spreading to new, previously healthy skin areas.
The incubation period is seven days, after which the active development of the disease takes place, turning into an acute form. If tests are performed and a diagnosis is made, streptodermia should be urgently started to treat in order to avoid complications. The course of the disease can be acute or chronic, superficial or deep. When the chronic form of the rash is localized near the existing sores or wounds.
How is streptoderma transmitted?
Why does streptoderma occur, what is it, and how to treat it? Most pathology occurs in young children from 2 to 7 years of age.
Provoke the onset of the disease can cuts, abrasions and scratches on the skin, bites of various insects, etc. damage to the skin through which the infection penetrates. Streptodermia is transmitted by household means, for example, through dishes and clothes, toys, etc. subjects that were affected by the affected child.
The causative agent of streptodermia is streptococcal bacteria (mainly beta-hemolytic pyogenic streptococcus of group A), active reproduction which on the skin leads to the appearance of impetigo, vulgar eczema and some other diseases, united by the concept of "streptoderma."
Different types of streptococcus can be found:
- on toys (especially soft or rarely washable);
- any dishes;
- on any clothing, both top and underwear, especially if it is not thoroughly washed and not ironed;
- in water and air, that is, a child of any age is constantly confronting him;
- on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes of another person (small and adult), which can be so-called healthy carrier (there are no symptoms of the disease) or have sore throat, otitis, erysipelas.
The causes of streptoderma may be as follows:
- Decreased immunity, in which even a small number of microbes can cause disease.
- Infringement of microflora in the intestine as a result of improper intake of antibacterial agents or inadequate nutrition.
- Neglect of sanitary and hygienic norms leads to the emergence of favorable conditions for the propagation of pathogens of the disease.
- Combing the skin with dermatoses leads to infection with streptococcus and the development of streptoderma.
Depending on the manifestations and nature of the currentStreptoderma is classified into the following types:
- Dry streptoderma, or simple lichen. Often affects children aged 3-7 years, manifested as flaky pink spots and skin pigmentation disorders.
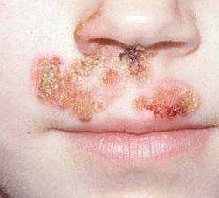
- Streptococcal impetigo. It is a bubble rash, surrounded by a red inflamed rim around the periphery. After their tearing, there are erosions on the skin, which are subsequently covered with scabs.
Factors contributing to the spread of rashes on the body are bathing and combing lesions. With excessive production of sebum and active perspiration, streptodermia manifests itself in the inguinal and behind-the-back folds. Such spreads of rashes on the body are most frequent in those who are overweight or have diabetes.
Symptoms of streptoderma
The incubation period of the disease is 7-10 days. The main symptom of streptodermia in children is the appearance on the skin of pink spots, covered with small scales. During the appearance of rashes, no subjective symptoms are usually felt. But sometimes itching can occur, an increase in body temperature, as well as an increase in the cervical lymph nodes, the affected skin becomes increasingly dry.
Stains with streptoderma can have completely different sizes, but most often in diameter they reach up to 4 cm. Eruptions are localized on the face, back, buttocks, arms and legs. After all the spots are available, a specific white trace remains for a certain time in their place. The concept of streptoderma includes several types of infectious skin lesions. Streptococci are pathogens of all types of disease.
Varieties of pathology:
- Streptococcal impetigo. The most common, classical form of the disease. Typical eruptions appear on the face, hands and feet. This form of streptoderma is the most limited, since the causative agent does not penetrate beyond the surface layer of skin that retains its protective functions and includes local mechanisms to limit inflammation. The appearance of the skin does not change much, only on the background of redness there are individual bubble elements (fliken), filled with a clear liquid. Their appearance is accompanied by itching. Soon the liquid becomes turbid, the vial is opened, dried and covered with a yellow crust. After removing the crust on the skin remain pigmented specks, which eventually disappear. The duration of the process is from 5 to 7 days. But if the child combs the itching elements, the pathogen spreads to healthy areas of the skin, the risk of complications increases and the recovery is delayed by 3-4 weeks.
- Bullous impetigo. The rash is localized on the upper and lower limbs (brushes, feet) and has a fairly solid diameter. After the opening of the vesicles in their place, ulcers develop, which can expand, capturing healthy areas of the skin.
- Streptococcal intertrigo. Most of the diseased are small children and fat people. Localization of foci - under the mammary glands, in the armpits, interannual or inguinal-femoral folds. Obesity affects the abdomen.
- Common lichen. It appears as a rash of bright pink color, with clear boundaries. The place of localization is the person. The rash may diminish in size under the influence of the sun. Those skin areas that were previously affected, can not sunbathe like the rest of the skin.
- Streptococcal galloping(a kind of slit-like impetigo) is characterized by the appearance of vesicles in the corners of the mouth. After the disappearance of the bubbles in their place, a cracks appear (slit-like erosion) rapidly becoming covered with a yellowish crust. Very often patients, especially children, accidentally tear off the crust, but it appears again.
- Streptococcal ecthima- a heavier leaking form of streptoderma affecting the deep layers of the skin. The disease proceeds with the formation of ulcerative necrotic lesion and scar. Ectima is often formed on the hands, feet and almost never on the face, as the face has a very good blood supply to the skin, allowing localized inflammation. It is in the case of ecthymia, as a rule, pronounced impairment of well-being, up to signs of an infectious-toxic shock, if the pathogen has got into the bloodstream.
With the timely treatment of symptoms of streptoderma, usually pass for 7 days. If you do not take adequate measures, the disease can cause such severe complications as psoriasis, scarlet fever, glomerulonephritis, microbial eczema. Sometimes the disease in chronic form even leads to infection of the blood.
Chronic form
Streptodermia in chronic form is characterized by a recurrent course and the development of large lesions (5-10 cm in diameter) of the lesions of the skin. The foci are clearly delimited spots with uneven, scalloped edges and exfoliating at the edges of the corneous layer of the epidermis; most often they are localized on the legs.
On the skin there are bubbles, after the opening of which large coats of a yellowish-brown color are formed. After removing the crust on the spot, there is a bright pink erosion, from the surface of which the serous-purulent exudate is abundantly separated. Between the relapses, the formation of new blisters stops, instead of crusts, peeling centers are formed with gray-yellow scales.
The long existence of an infectious focus, as well as the increased sensitivity of cutaneous cover to microbes can lead to the transition of the disease from chronic streptoderma to microbial eczema. Characteristic features of this process are the appearance of eczematous wells, the change in the boundaries of the lesion (at eczema they become uneven, vague).
How does streptoderma begin?
We offer to view detailed photos to know how it looks and begins streptodermia in a child, as well as an adult.
Diagnostics
In order to know how to cure streptodermia, you must put an accurate diagnosis, because such a disease can be implied and under other diseases. These are erysipelas, vulgar ectima, chronic diffuse streptoderma and others. The diagnosis of "streptoderma" is established on the basis of anamnestic data (contact with a sick person, an outbreak of a disease in the team) and visual inspection (characteristic bubbles and yellowish-honey crusts after their opening).
From laboratory methods use:
- smear microscopy of the affected area of the skin;
- bacteriological analysis (seeding crusts on nutrient media).
Microscopy and bacussis should be performed before antibiotic treatment and provided there is no self-treatment.
Treatment of streptoderma
In those cases when the symptoms of streptoderma are small, and do not worsen the general condition of the patient, then in the treatment Streptodermia in children with good immunity usually uses local therapy at home. It is an autopsy of abscesses and the subsequent treatment of lesions with aniline dyes. After that, dry patches with disinfectants are applied to the diseased areas. Zaeda is lubricated with silver nitrate.
In chronic processes for the treatment of streptoderma in children and adults, complex conservative therapy is indicated:
- Reception of antibiotics. Optimum in this situation, semi-synthetic penicillins are considered, and in the case of resistance to the organism, antibiotics of the reserve are considered. Usually, Amoxiclav, Augmentin, Ceporin, Lincomycin are used. Reserve - macrolides Azithromycin or Erythromycin.
- Injection of immunomodulators and vitamins. Gamma globulin, vitamin complexes B, A, C, as well as polyglobulin are used.
- Taking medications necessary to restore intestinal microfloraafter antibiotic therapy (probiotics): linex, dyufolac.
- Admission of multivitamins(1-2 months + repeat): complimentary, centrum, vitrum, multitabs or others.
- Treatment with topical preparations, which are applied to cleansed skin twice a day. These include alcohol antiseptic solutions (5% levomycetin alcohol, fucorcin, etc.), myramistine (chlorhexidine) solution, potassium permanganate solution. Ointments with antibiotics are prescribed: lincomycin, erythromycin, levomecol and others.
How to treat streptoderma in a child? Follow the basic recommendations:
- limit the contacts of a sick child to healthy peers;
- high temperature - the basis for bed rest;
- banned rubbing and bathing - the infection can spread to new sites;
- watch for the length of the nails and the cleanliness of the hands of the child;
- every day, change your underwear and bed linen;
- wash the floor thoroughly, ventilate the room;
- distract the child, do not let us comb the sores;
- prepare diet food for the patient;
- bake dishes or cook.
In the focus of the infection, quarantine is mandatory - the children are separated for at least 10 days (for the maximum duration of the incubation period). In the process of treatment, it is mandatory to use a therapeutic diet consisting of easily digestible and nutritious food, in which it is necessary to limit sweets, fatty and spicy foods.
Streptoderma treatment at home
The disease is effectively treated with folk remedies, including the use of decoction of herbs (chamomile, oak bark) as bandages. The whole period of treatment is forbidden to use hygienic baths and showers. We replace these procedures with wipes soaked in a tincture of chamomile.
Complications and prognosis
The symptoms of streptoderma with adequate treatment disappear in a week, but in some cases (with weakened immunity or the presence of chronic diseases) complications are possible:
- transition to a chronic form;
- teardrop-shaped psoriasis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- rheumatism;
- myocarditis;
- microbial eczema;
- scarlet fever;
- furuncles and phlegmon;
- Septicemia is a blood poisoning in which a huge amount of streptococci is circulating.
The prognosis for this disease is favorable, but after suffering a deep form of streptoderma, cosmetic defects remain.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.
Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



